What is transactional email?

Transactional email refers to automated messages sent to individuals based on events related to their interactions with a website.
These emails are typically triggered by users.
Common examples of transactional emails include:
- Order confirmations: Sent after a customer makes a purchase to confirm the details of the transaction.
- Website contact form inquiries
- Shipping notifications: Informing customers when their orders have been shipped and providing tracking information.
- Password resets: Emails sent to users who request to reset their passwords for security purposes.
- Account notifications: Alerts about changes to account settings, such as email address changes or security alerts.
Transactional emails are distinct from promotional emails, which are typically aimed at marketing products or services. Transactional emails have higher open and engagement rates compared to promotional emails.
Improving Sender Reputation
Futurised recommends Postmark.
Postmark is an Email Service Provider (ESP) that specialises in transactional email delivery.
If you don’t have good sender reputation, you’ll experience issues with emails going to spam folders or being marked as unverified.
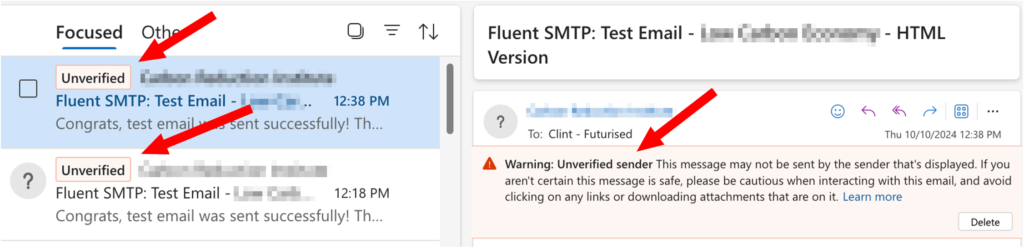
Postmark sends transactional emails through a separate IP address keeping those emails away from marketing email streams. This is what allows Postmark to keep their transactional IP addresses clean, unlike other ESPs that merge transactional and marketing message streams together.
Key differences between Postmark and other ESPs
- Postmark separates email traffic through Message Streams. Transactional
and broadcast (bulk) traffic does not mix in Postmark, including IP ranges. - You can manage suppression lists and unsubscribes through Postmark, and add unsubscribe links to your emails. Learn more in our help doc.
- Postmark does not recommend using dedicated IPs for most senders (save money as a dedicated IP address is not needed).
- When a non-200 response code is received, Postmark retries 10 times over a 10.5 hour period, with growing intervals from 1 minute to 6 hours. If all of the retries have failed, your inbound activity page will show the message has a processing error.
- Postmark normalises email content to UTF-8 instead of needing to manually transcode email content.
Other ESPs (Sendgrid, Brevo)
- They allow a lot of free account users to send marketing emails, increasing the possibility of the sending IP address being added to blacklists and your emails going to spam folders or hard bouncing.
- They will recommend purchasing a dedicated IP address at approx $400 per year if you experience issues with the IP being blacklisted due to other users of the system.
Postmark Message Streams
Postmark separates email traffic through Message Streams, meaning that transactional and broadcast traffic never intersects in Postmark. Transactional message streams are for messages that are usually unique and triggered by a user action like a welcome email, password reset, or receipts. Transactional streams do not support broadcast messages. Broadcast message streams are for bulk messages that sent to multiple recipients at once like announcements, newsletters, or other application emails.
Sender Signatures and Verified Domains
In Postmark you need to have a confirmed sender signature or verified domain for each email address you want to send from. Sender signatures are individual email addresses that are authorised for sending via a confirmation email sent to that address. Adding and verifying a domain using a DKIM record lets you send from any email address on that domain.
Do you need a dedicated IP for transactional emails?
The importance of dedicated IP addresses in email delivery has diminished over the past five years, as domain reputation has become increasingly significant. Initially, the shift towards domain-based reputation, particularly with DKIM, was emerging, and the responsibility of Email Service Providers (ESPs) to manage their networks was growing. ISPs are relying less on IP reputation and emphasising strategies for optimising shared IP environments. These strategies include using custom DKIM signatures, personalising return-paths, and maintaining consistent branding in emails to enhance recognition and reduce spam reports.
Despite the shift towards domain reputation, IP addresses still play a role, especially for corporate networks that depend on blacklists and IP reputation. ESPs must ensure their email streams are clean to support domain reputation effectively.
While dedicated IPs are available for high-volume senders, the focus remains on transactional emails, which yield higher engagement rates and better delivery outcomes.
ISPs are becoming less reliant on IP reputation. Here are some great points on how to make the best of a shared IP environment:
- Use your own domain in the DKIM signature. Domain Verification builds on the advantages of DKIM.
- Take advantage of personalisation of the return-path. You can use custom return-path settings for this, which also helps you align with DMARC policies.
- Brand your emails and use consistent design elements. This helps ensure that your emails are easily recognisable by filters as well as recipients so they don’t report them as spam.
Webhooks
Setup a bounce webhook to be notified when an email bounces.
Recent Posts
The Winning SEO Formula for Roofers: Why You Need a Page for Every Service in Every Suburb
Rovo Dev CLI installation and prompts
What is transactional email?
How to Regain Your Lost Top Search Rankings
Microsoft 365 Family Usage
Prompts for Blogs ChatGPT
How Bing Image Creator lets you generate images from words
Free to use images for commercial use
Historical Optimisation: How to Choose the Right Content to Update
AU Direct Registrations and Applications